distribution shape histograms and box plots Histograms and box plots are very similar in their ability to visualize and describe numeric data. Although histograms are better in determining the underlying distribution of the data, box plots . Luckily, there are many different in-demand items that you can make on a CNC machine, from a simple cell phone stand to a complete chess set. Here, we’ll dive into the world of CNC projects and highlight some of the most profitable options.
0 · matching box plots with histograms
1 · explain box plot with example
2 · difference between boxplot and histogram
3 · combination histogram and boxplot
4 · box plot for dummies
5 · box and whisker vs histogram
6 · box and whisker plots explained
7 · box and whisker plot without
In the modern design world, white cabinets paired with stainless steel appliances is a match made in heaven because of the clean, sophisticated elegance it introduces into your kitchen. Consider the undertones when selecting the right shade of white. Reflectivity is key – glossy finishes on cabinets enhance brightness.
Histograms and box plots are very similar in their ability to visualize and describe numeric data. Although histograms are better in determining the underlying distribution of the data, box plots .The Binary Distribution (or Bernoulli distribution) is a discrete probability .A process is described as a cross-functional when it involves multiple departments, .Different graphs can reveal different characteristics of your data such as the .
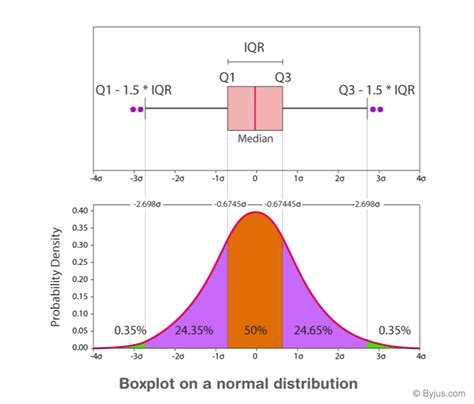
Histograms and box plots can be quite useful in suggesting the shape of a probability distribution. Here, we'll concern ourselves with three possible shapes: symmetric, skewed left, or skewed . Box plots provide basic information about a distribution. For example, a distribution with a positive skew would have a longer whisker in the positive direction than in the negative .
Histograms and box plots can be quite useful in suggesting the shape of a probability distribution. Here, we'll concern ourselves with three possible shapes: symmetric, skewed left, or skewed . In descriptive statistics, a box plot or boxplot (also known as a box and whisker plot) is a type of chart often used in explanatory data analysis. Box plots visually show the distribution of numerical data and skewness by .

sheet metal screw part number specification
In short: Barplots, histograms and boxplots are commonly used in (descriptive) statistics to visualise distribution of numerical data with two variables (typically the response variable on the X axis and the categorical explanatory .The shape of a distribution is described by its number of peaks and by its possession of symmetry, its tendency to skew, or its uniformity. (Distributions that are skewed have more points plotted on one side of the graph than on the other.)You can tell the shape of the histogram (distribution) - in many cases at least - by just looking the box plot, and you can also estimate whether the mean is less than or greater than the median.We can describe the shape of distributions as symmetric, skewed, bell-shaped, bimodal, or uniform. Here is a dot plot, histogram, and box plot representing the distribution of the same .
Histograms and box plots are very similar in their ability to visualize and describe numeric data. Although histograms are better in determining the underlying distribution of the data, box plots allow the comparison of multiple datasets as they are less detailed and take up less space.Histograms and box plots can be quite useful in suggesting the shape of a probability distribution. Here, we'll concern ourselves with three possible shapes: symmetric, skewed left, or skewed right. Box plots provide basic information about a distribution. For example, a distribution with a positive skew would have a longer whisker in the positive direction than in the negative direction. A larger mean than median would also indicate a positive skew.A box plot, sometimes called a box and whisker plot, provides a snapshot of your continuous variable’s distribution. They particularly excel at comparing the distributions of groups within your dataset.
Histograms and box plots can be quite useful in suggesting the shape of a probability distribution. Here, we'll concern ourselves with three possible shapes: symmetric, skewed left, or skewed right.
In descriptive statistics, a box plot or boxplot (also known as a box and whisker plot) is a type of chart often used in explanatory data analysis. Box plots visually show the distribution of numerical data and skewness by displaying the data quartiles (or percentiles) and averages.
In short: Barplots, histograms and boxplots are commonly used in (descriptive) statistics to visualise distribution of numerical data with two variables (typically the response variable on the X axis and the categorical explanatory variable on the Y axis).The shape of a distribution is described by its number of peaks and by its possession of symmetry, its tendency to skew, or its uniformity. (Distributions that are skewed have more points plotted on one side of the graph than on the other.)You can tell the shape of the histogram (distribution) - in many cases at least - by just looking the box plot, and you can also estimate whether the mean is less than or greater than the median.We can describe the shape of distributions as symmetric, skewed, bell-shaped, bimodal, or uniform. Here is a dot plot, histogram, and box plot representing the distribution of the same data set. This data set has a symmetric distribution.
Histograms and box plots are very similar in their ability to visualize and describe numeric data. Although histograms are better in determining the underlying distribution of the data, box plots allow the comparison of multiple datasets as they are less detailed and take up less space.
Histograms and box plots can be quite useful in suggesting the shape of a probability distribution. Here, we'll concern ourselves with three possible shapes: symmetric, skewed left, or skewed right. Box plots provide basic information about a distribution. For example, a distribution with a positive skew would have a longer whisker in the positive direction than in the negative direction. A larger mean than median would also indicate a positive skew.A box plot, sometimes called a box and whisker plot, provides a snapshot of your continuous variable’s distribution. They particularly excel at comparing the distributions of groups within your dataset.
Histograms and box plots can be quite useful in suggesting the shape of a probability distribution. Here, we'll concern ourselves with three possible shapes: symmetric, skewed left, or skewed right.
In descriptive statistics, a box plot or boxplot (also known as a box and whisker plot) is a type of chart often used in explanatory data analysis. Box plots visually show the distribution of numerical data and skewness by displaying the data quartiles (or percentiles) and averages. In short: Barplots, histograms and boxplots are commonly used in (descriptive) statistics to visualise distribution of numerical data with two variables (typically the response variable on the X axis and the categorical explanatory variable on the Y axis).
The shape of a distribution is described by its number of peaks and by its possession of symmetry, its tendency to skew, or its uniformity. (Distributions that are skewed have more points plotted on one side of the graph than on the other.)You can tell the shape of the histogram (distribution) - in many cases at least - by just looking the box plot, and you can also estimate whether the mean is less than or greater than the median.
matching box plots with histograms
House lawmakers will now be required to go through a metal detector security screening before being allowed to enter the chamber. The new safety protocol announced Tuesday from the acting.
distribution shape histograms and box plots|explain box plot with example