distributions box plots Review of box plots, including how to create and interpret them. To install a spur from a junction box, you require a 30amp junction box. Locate the cable of the ring main as close to the new socket as possible. Lift the floorboards and locate the cable that runs closest to your new socket.
0 · understanding box plots for dummies
1 · how to make a box and whisker plot
2 · different types of box plots
3 · describing shape of box plots
4 · boxplot shape of distribution
5 · box plot for normal distribution
6 · box plot distribution interpretation
7 · box and whisker chart type
Wrought Iron Window Boxes, Window Box Planters, and Metal Flower Boxes! Looking for affordable wrought iron window boxes? We offer seven (7) sizes of window box hayracks .
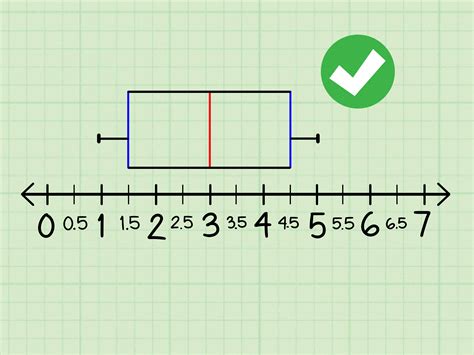
What is a Box Plot? A box plot, sometimes called a box and whisker plot, provides a snapshot of your continuous variable’s distribution. They particularly excel at comparing the distributions of groups within your dataset. A box plot .A box plot is an easy method to display the set of data distribution in terms of quartiles. Visit BYJU’S to learn its definition, and learn how to find out the five-number summary of box plot with Examples.Box plots are used to show distributions of numeric data values, especially when you want to compare them between multiple groups. They are built to provide high-level information at a .Although box plots may seem more primitive than histograms or kernel density estimates, they do have a number of advantages. First, the box plot enables statisticians to do a quick graphical examination on one or more data sets. Box-plots also take up less space and are therefore particularly useful for comparing distributions between several groups or sets of data in parallel (see Figure 1 f.
Review of box plots, including how to create and interpret them. A box plot, also known as a box-and-whisker plot, is a graphical representation of the distribution of a dataset. It summarizes key statistics such as the median, quartiles, and outliers, providing insights into the spread and .A boxplot, also known as a box plot, box plots, or box-and-whisker plot, is a standardized way of displaying the distribution of a data set based on its five-number summary of data points: the “minimum,” first quartile [Q1], median, .In this explainer, we will learn how to compare two data set distributions using box plots. Box plots, which are sometimes called box-and-whisker plots, can be a good way to visualize .

In this comprehensive guide, we will walk you through the key components of box plots and show you how to interpret them effectively. A box plot, also known as a box-and-whisker plot, is a standardized way of displaying the distribution of . Box plots visually show the distribution of numerical data and skewness by displaying the data quartiles (or percentiles) and averages. Box plots show the five-number summary of a set of data: including the minimum score, first (lower) quartile, median, third (upper) quartile, and maximum score.What is a Box Plot? A box plot, sometimes called a box and whisker plot, provides a snapshot of your continuous variable’s distribution. They particularly excel at comparing the distributions of groups within your dataset. A box plot displays a ton of information in a simplified format.A box plot is an easy method to display the set of data distribution in terms of quartiles. Visit BYJU’S to learn its definition, and learn how to find out the five-number summary of box plot with Examples.
Box plots are used to show distributions of numeric data values, especially when you want to compare them between multiple groups. They are built to provide high-level information at a glance, offering general information about a group of .First, the box plot enables statisticians to do a quick graphical examination on one or more data sets. Box-plots also take up less space and are therefore particularly useful for comparing distributions between several groups or sets of data in parallel (see Figure 1 for an example).
Review of box plots, including how to create and interpret them. A box plot, also known as a box-and-whisker plot, is a graphical representation of the distribution of a dataset. It summarizes key statistics such as the median, quartiles, and outliers, providing insights into the spread and central tendency of the data.A boxplot, also known as a box plot, box plots, or box-and-whisker plot, is a standardized way of displaying the distribution of a data set based on its five-number summary of data points: the “minimum,” first quartile [Q1], median, third quartile [Q3] and “maximum.”In this explainer, we will learn how to compare two data set distributions using box plots. Box plots, which are sometimes called box-and-whisker plots, can be a good way to visualize differences among groups that have been measured on the same variable.
In this comprehensive guide, we will walk you through the key components of box plots and show you how to interpret them effectively. A box plot, also known as a box-and-whisker plot, is a standardized way of displaying the distribution of data based on a five-number summary: minimum, first quartile (Q1), median, third quartile (Q3), and maximum. Box plots visually show the distribution of numerical data and skewness by displaying the data quartiles (or percentiles) and averages. Box plots show the five-number summary of a set of data: including the minimum score, first (lower) quartile, median, third (upper) quartile, and maximum score.What is a Box Plot? A box plot, sometimes called a box and whisker plot, provides a snapshot of your continuous variable’s distribution. They particularly excel at comparing the distributions of groups within your dataset. A box plot displays a ton of information in a simplified format.
A box plot is an easy method to display the set of data distribution in terms of quartiles. Visit BYJU’S to learn its definition, and learn how to find out the five-number summary of box plot with Examples.Box plots are used to show distributions of numeric data values, especially when you want to compare them between multiple groups. They are built to provide high-level information at a glance, offering general information about a group of .First, the box plot enables statisticians to do a quick graphical examination on one or more data sets. Box-plots also take up less space and are therefore particularly useful for comparing distributions between several groups or sets of data in parallel (see Figure 1 for an example).
Review of box plots, including how to create and interpret them. A box plot, also known as a box-and-whisker plot, is a graphical representation of the distribution of a dataset. It summarizes key statistics such as the median, quartiles, and outliers, providing insights into the spread and central tendency of the data.A boxplot, also known as a box plot, box plots, or box-and-whisker plot, is a standardized way of displaying the distribution of a data set based on its five-number summary of data points: the “minimum,” first quartile [Q1], median, third quartile [Q3] and “maximum.”In this explainer, we will learn how to compare two data set distributions using box plots. Box plots, which are sometimes called box-and-whisker plots, can be a good way to visualize differences among groups that have been measured on the same variable.
sheet metal flaring tool
understanding box plots for dummies
how to make a box and whisker plot
different types of box plots
EMT allows use of normal size wires with up to 4 circuits per conduit (the equivalent of 8 if you use multi-wire branch circuits). 1/2" EMT is easy to work with, cuts with any hacksaw, deburrs with your multi-tool stripper, and the fittings are dirt cheap. Combine that with $1.00 Handy-boxes or 4x4 boxes, and it's easy going.
distributions box plots|understanding box plots for dummies