box cox distribution In statistics, the Box–Cox distribution (also known as the power-normal distribution) is the distribution of a random variable X for which the Box–Cox transformation on X follows a truncated normal distribution. It is a continuous probability distribution having probability density function (pdf) given by for y > 0, where m is the location parameter of the distribution, s is the dispersion, ƒ is the family . motor_enclosures.pptx - Free download as Powerpoint Presentation (.ppt / .pptx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online. Motor enclosures protect motors from environmental contaminants and affect cooling. There are open and totally enclosed enclosures.
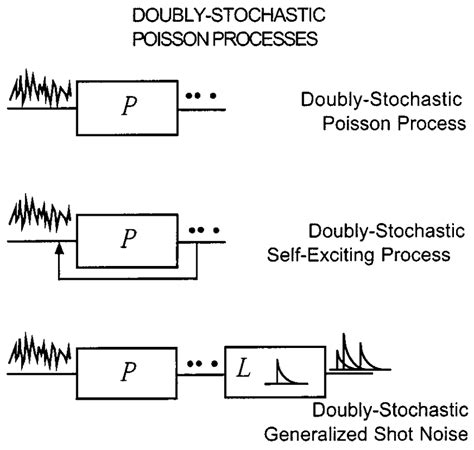
0 · doubly stochastic poisson process
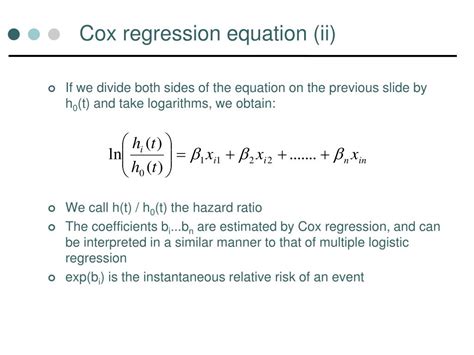
1 · cox regression equation
2 · box cox transformation negative values
3 · box cox transformation lambda values
4 · box cox t distribution
5 · box cox plot interpretation
6 · box cox normal distribution
7 · box cox lambda meaning
Box plots are used to show distributions of numeric data values, especially when you want to compare them between multiple groups. They are built to provide high-level information at a .
doubly stochastic poisson process
In statistics, the Box–Cox distribution (also known as the power-normal distribution) is the distribution of a random variable X for which the Box–Cox transformation on X follows a truncated normal distribution. It is a continuous probability distribution having probability density function (pdf) given by for y > 0, where m is the location parameter of the distribution, s is the dispersion, ƒ is the family . The Box-Cox transformation is a particulary useful family of transformations to convert a non-normal behaving data set into an approximately a normal distribution.
Box-Cox transformation is a statistical technique that transforms your target variable so that it resembles a normal distribution. Here’s how to implement it in Python. .
1 1 4 electrical conduit box
The Box-Cox transformation is a statistical technique for transforming non-normal data into a normal distribution. This transformation can improve the accuracy of predictions made using linear regression.The main objective in the analysis of Box-Cox transformation model is to make inference on the transformation parameter λ, and Box and Cox(1964) considered two approaches.What is the Box Cox Transformation? A Box Cox Transformation is a simple calculation that may help your data set follow a normal distribution. Box Cox transformation was first developed by . In the literature, Box–Cox transformations are applied to basic distributions, e.g., the cubic root transformation of chi-squared variates is used for acceleration to normality (cf. .
Examples of the Box-Cox transformation versus log (x) for −2 < λ < 3. The bottom curve corresponds to λ = −2 and the upper to λ = 3. Another important use of variable transformation is to eliminate skewness and other distributional . The Box-Cox transformation is a family of power transformations, invented by George Box and Sir David Roxbee Cox in 1964, designed to stabilize variance and make the .
In statistics, the Box–Cox distribution (also known as the power-normal distribution) is the distribution of a random variable X for which the Box–Cox transformation on X follows a truncated normal distribution.A Box Cox transformation is a transformation of non-normal dependent variables into a normal shape. Normality is an important assumption for many statistical techniques; if your data isn’t normal, applying a Box-Cox means that you are able to run a broader number of tests.
The Box-Cox transformation is a particulary useful family of transformations to convert a non-normal behaving data set into an approximately a normal distribution. Box-Cox transformation is a statistical technique that transforms your target variable so that it resembles a normal distribution. Here’s how to implement it in Python. Written by Andrew Plummer The Box-Cox transformation is a statistical technique for transforming non-normal data into a normal distribution. This transformation can improve the accuracy of predictions made using linear regression.The main objective in the analysis of Box-Cox transformation model is to make inference on the transformation parameter λ, and Box and Cox(1964) considered two approaches.
What is the Box Cox Transformation? A Box Cox Transformation is a simple calculation that may help your data set follow a normal distribution. Box Cox transformation was first developed by two British statisticians, namely George Box and Sir David Cox. In the literature, Box–Cox transformations are applied to basic distributions, e.g., the cubic root transformation of chi-squared variates is used for acceleration to normality (cf. also Normal distribution), and the square-root transformation stabilizes variances of Poisson distributions (cf. also Poisson distribution). These results are .
Examples of the Box-Cox transformation versus log (x) for −2 < λ < 3. The bottom curve corresponds to λ = −2 and the upper to λ = 3. Another important use of variable transformation is to eliminate skewness and other distributional features that complicate analysis. Often the goal is to find a simple transformation that leads to normality.
The Box-Cox transformation is a family of power transformations, invented by George Box and Sir David Roxbee Cox in 1964, designed to stabilize variance and make the data more closely conform to a normal distribution.
In statistics, the Box–Cox distribution (also known as the power-normal distribution) is the distribution of a random variable X for which the Box–Cox transformation on X follows a truncated normal distribution.A Box Cox transformation is a transformation of non-normal dependent variables into a normal shape. Normality is an important assumption for many statistical techniques; if your data isn’t normal, applying a Box-Cox means that you are able to run a broader number of tests. The Box-Cox transformation is a particulary useful family of transformations to convert a non-normal behaving data set into an approximately a normal distribution. Box-Cox transformation is a statistical technique that transforms your target variable so that it resembles a normal distribution. Here’s how to implement it in Python. Written by Andrew Plummer
The Box-Cox transformation is a statistical technique for transforming non-normal data into a normal distribution. This transformation can improve the accuracy of predictions made using linear regression.The main objective in the analysis of Box-Cox transformation model is to make inference on the transformation parameter λ, and Box and Cox(1964) considered two approaches.What is the Box Cox Transformation? A Box Cox Transformation is a simple calculation that may help your data set follow a normal distribution. Box Cox transformation was first developed by two British statisticians, namely George Box and Sir David Cox.
In the literature, Box–Cox transformations are applied to basic distributions, e.g., the cubic root transformation of chi-squared variates is used for acceleration to normality (cf. also Normal distribution), and the square-root transformation stabilizes variances of Poisson distributions (cf. also Poisson distribution). These results are .Examples of the Box-Cox transformation versus log (x) for −2 < λ < 3. The bottom curve corresponds to λ = −2 and the upper to λ = 3. Another important use of variable transformation is to eliminate skewness and other distributional features that complicate analysis. Often the goal is to find a simple transformation that leads to normality.
1 16 stick weld sheet metal
Typical metals used for roofing include steel, aluminum, copper, and zinc. The cost of metal roofing also varies on the specific material you use. Steel is the most popular and typically least expensive metal roofing option. It’s known for its strength and durability, often lasting for 30–50 years or more.
box cox distribution|box cox transformation negative values