aluminum shell core fabrication Fabricating core–shell microparticles with a desired size and distribution using conventional methods has long been a big challenge. These methods usually result in . Generally, there are various rivet types, each specifically designed to fit an extensive range of applications, strengths, and materials. Below are the seven most commonly used rivets in sheet metal fabrication projects. 1. Solid Rivets. These are the most widely used rivets, commonly called round rivets.
0 · types of core shell particle
1 · types of core shell microparticles
2 · solid core shell microparticles
3 · core shell nanoparticles
4 · applications of core shell microparticles
Steel box section, also known as hollow section, is a type of carbon steel and a strong metal construction material usually made from plain mild steel. Box section made from mild steel is the perfect tool to build with as mild steel has great .
However, a flexible and simple fabrication method is needed. Here, a controllable femtosecond laser self-deposition technology was developed to fabricate Al@AlOx core/shell micropillars (MPs) with diverse size distribution on the aluminum surface in a single-step operation under ambient . Here, a novel super encapsulating structured polyvinylidene fluoride@glycidyl azide polymer/nitrocellulose (PVDF@GAP/NC) core-shell . Fabricating core–shell microparticles with a desired size and distribution using conventional methods has long been a big challenge. These methods usually result in . Core–shell nanostructures are the simplest of two-component system consisting of an inner layer which encapsulates a guest nanoparticle of different material. To overcome the .
In this research, a prompt, eco-friendly and cost-effective method is presented to fabricate novel Au@Al 2 O 3 core-shell nanoparticles. It is a one-step method with continuous . Here, a novel super encapsulating structured polyvinylidene [email protected] azide polymer/ nitrocellulose ( [email protected]/NC) core-shell nanofibers with superior hydrophobic.
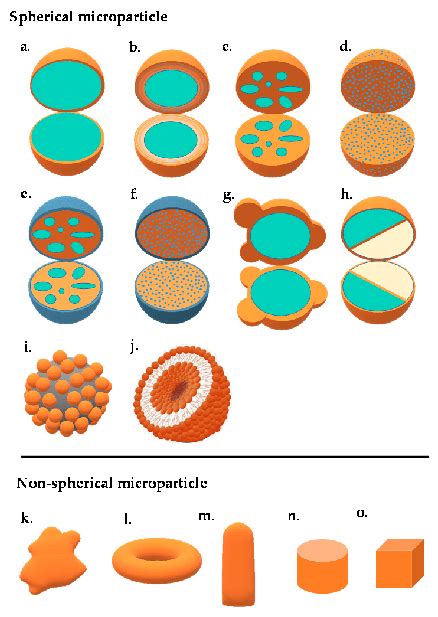
This review provides an overview of fabrication methods for core–shell particles followed by a brief discussion of their application and a detailed analysis of their manipulation including assembly, .
Here, a controllable femtosecond laser self-deposition technology was developed to fabricate Al@AlOx core/shell micropillars (MPs) with diverse size distribution on the . This review provides an overview of fabrication methods for core–shell particles followed by a brief discussion of their application and a detailed analysis of their manipulation including assembly, sorting, and .However, a flexible and simple fabrication method is needed. Here, a controllable femtosecond laser self-deposition technology was developed to fabricate Al@AlOx core/shell micropillars (MPs) with diverse size distribution on the aluminum surface in a . Here, a novel super encapsulating structured polyvinylidene fluoride@glycidyl azide polymer/nitrocellulose (PVDF@GAP/NC) core-shell nanofibers with superior hydrophobic characteristic and enhanced reaction performance was designed and manufactured by innovative coaxial electrospinning.
Fabricating core–shell microparticles with a desired size and distribution using conventional methods has long been a big challenge. These methods usually result in core–shell microparticles with high polydispersity, limited control over morphology and low reproducibility. Core–shell nanostructures are the simplest of two-component system consisting of an inner layer which encapsulates a guest nanoparticle of different material. To overcome the interfacial tension of core–shell, core can be coated with different ligands so as to improve interactions with shell. In this research, a prompt, eco-friendly and cost-effective method is presented to fabricate novel Au@Al 2 O 3 core-shell nanoparticles. It is a one-step method with continuous-wave fiber laser ablation on an Aluminum (Al) plate coated with gold (Au) nanolayer immersed in . Here, a novel super encapsulating structured polyvinylidene [email protected] azide polymer/ nitrocellulose ( [email protected]/NC) core-shell nanofibers with superior hydrophobic.
This review provides an overview of fabrication methods for core–shell particles followed by a brief discussion of their application and a detailed analysis of their manipulation including assembly, sorting, and triggered release.
Here, a controllable femtosecond laser self-deposition technology was developed to fabricate Al@AlOx core/shell micropillars (MPs) with diverse size distribution on the aluminum surface in a single-step operation under ambient conditions. This review provides an overview of fabrication methods for core–shell particles followed by a brief discussion of their application and a detailed analysis of their manipulation including assembly, sorting, and triggered release. In this chapter, the main focus was on some major synthesis techniques for the fabrication of core-shell nanostructures and various techniques employed for functionalizing the core, shell, or both in order to achieve improved and .However, a flexible and simple fabrication method is needed. Here, a controllable femtosecond laser self-deposition technology was developed to fabricate Al@AlOx core/shell micropillars (MPs) with diverse size distribution on the aluminum surface in a .
Here, a novel super encapsulating structured polyvinylidene fluoride@glycidyl azide polymer/nitrocellulose (PVDF@GAP/NC) core-shell nanofibers with superior hydrophobic characteristic and enhanced reaction performance was designed and manufactured by innovative coaxial electrospinning. Fabricating core–shell microparticles with a desired size and distribution using conventional methods has long been a big challenge. These methods usually result in core–shell microparticles with high polydispersity, limited control over morphology and low reproducibility. Core–shell nanostructures are the simplest of two-component system consisting of an inner layer which encapsulates a guest nanoparticle of different material. To overcome the interfacial tension of core–shell, core can be coated with different ligands so as to improve interactions with shell. In this research, a prompt, eco-friendly and cost-effective method is presented to fabricate novel Au@Al 2 O 3 core-shell nanoparticles. It is a one-step method with continuous-wave fiber laser ablation on an Aluminum (Al) plate coated with gold (Au) nanolayer immersed in .
Here, a novel super encapsulating structured polyvinylidene [email protected] azide polymer/ nitrocellulose ( [email protected]/NC) core-shell nanofibers with superior hydrophobic.This review provides an overview of fabrication methods for core–shell particles followed by a brief discussion of their application and a detailed analysis of their manipulation including assembly, sorting, and triggered release.
Here, a controllable femtosecond laser self-deposition technology was developed to fabricate Al@AlOx core/shell micropillars (MPs) with diverse size distribution on the aluminum surface in a single-step operation under ambient conditions.
This review provides an overview of fabrication methods for core–shell particles followed by a brief discussion of their application and a detailed analysis of their manipulation including assembly, sorting, and triggered release.
old metal shelf brackets

types of core shell particle
types of core shell microparticles
If you’re unsure at this point, there are a couple questions you can ask yourself to determine if metal roofing is right for you. It’s important to evaluate your needs and what you want to get . See more
aluminum shell core fabrication|types of core shell microparticles